
Canadian Earthquake Detector Has Deep-Sea Edge over U.S. Rival
Seafloor instruments will monitor seismic activity very close to the Cascadia fault

Seafloor instruments will monitor seismic activity very close to the Cascadia fault

More particulate matter in the air can build stronger, longer-lasting thunderstorms over the tropics, leading to more extreme storms. Christopher Intagliata reports.

The candidate said California has “no drought” and that water farmers need is being used to protect a “three-inch fish”

Network of deep-water observatories streams data in real time

Molten rock accumulates in a magma chamber outside the North Island’s main volcanoes

How drying forests and lightning may have turned fire from a primal threat into a life-sustaining object of reverence

The fault has shifted approximately 700 kilometers over the past 25 million years

Evidence indicates that waves as tall as skyscrapers and thousands of kilometers wide once washed over the Red Planet.

Evidence confirms dramatic climate change effects in the Solomon Islands

Less snow and warmer spring mean more acres burned

Film and book reviews from Scientific American’s May 2016 issue

Heavy rainstorms, tied to global warming, will not send gravelly, stony rivers raging over the landscape

As hoped-for precipitation from El Niño falls short, Los Angeles resorts to a controversial method to reap water from the sky

The devastating natural disaster in Fort McMurray is “consistent” with climate change

Country plans to “de-stock its parks” and seeks buyers who can manage wildlife

Water scarcity poses a greater risk of turmoil under global warming, the World Bank argues

The bugs kill trees but also reduce accumulated “fuel”

A year after a devastating earthquake triggered killer avalanches and rock falls in Nepal, scientists are wiring up mountainsides to forecast hazards
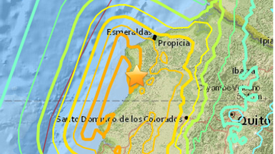
This region, where the ground beneath the Pacific is shoving underneath South America, produced the biggest earthquake ever recorded—and built the Andes

A shallow center made the magnitude 6.4 earthquake more dangerous
Support science journalism.

Thanks for reading Scientific American. Knowledge awaits.
Already a subscriber? Sign in.
Thanks for reading Scientific American. Create your free account or Sign in to continue.
Create Account