
New Tool Helps Predict Where Wildfire Smoke Will Blow
Scientists are working on ways to better anticipate the pathways—and health dangers—of drifting wildfire smoke

Scientists are working on ways to better anticipate the pathways—and health dangers—of drifting wildfire smoke

A new technique destroys persistent PFAS without requiring high pressures and temperatures

In the U.S., Black and Latino men who have sex with men are most vulnerable to monkeypox

Smoke from burning cities would engulf Earth after a nuclear war, causing worldwide crop failures and starvation, models show
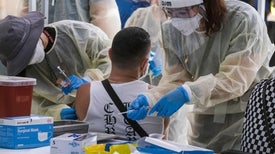
Frequently asked questions about how monkeypox spreads, who’s most at risk, and what vaccines and treatments are available

Industry-related groups say plastic is a safe material to replace lead pipes, but some researchers and health advocates are not so sure

Scientists and medical experts weigh in on how to recognize the signs of heat-related illness and avoid the worst health impacts from increasingly intense heat waves

The Langya virus, which is related to the Nipah and Hendra viruses, has infected at least 35 people in China in the two years before 2021
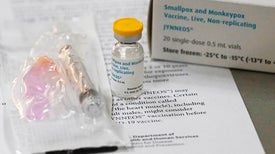
A virologist explains how they work, who can get them and how well they prevent infection
What the virus is, how it spreads, and how it is being handled: here’s what you need to know about monkeypox

Children “are not little adults”—they have more trouble regulating temperature than adults do

We’ve swung between fear and denial for too long and need to talk about this disease from a different perspective

Evidence-based solutions to firearm safety range from banning assault weapons to increasing green spaces

Blistering temperatures were ranked as a Category 3—the most severe tier—in Seville, Spain’s new heat wave system
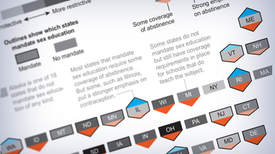
States that protect abortion rights tend to have more comprehensive sex ed policies

Tens of millions of Americans sweltered under heat advisories over the weekend

An infectious disease doctor explains what Biden’s medical team will be doing to treat the president’s case of COVID
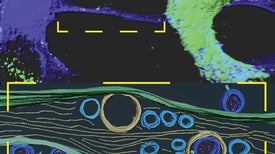
Nanotubes may provide a cunning answer to the mystery of how the virus that causes COVID infects neurons and produces long-lasting neurological symptoms
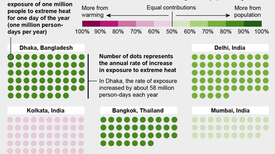
Population growth, climate change and the urban heat island effect are combining to put more people at risk

Events with extreme temperatures and humidity are occurring twice as often now as they were 40 years ago
Support science journalism.

Thanks for reading Scientific American. Knowledge awaits.
Already a subscriber? Sign in.
Thanks for reading Scientific American. Create your free account or Sign in to continue.
Create Account