
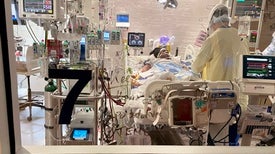
Can Drugs Reduce the Risk of Long COVID? What Scientists Know So Far
Researchers are trying to establish whether existing COVID-19 vaccines and treatments can prevent lasting symptoms

Researchers are trying to establish whether existing COVID-19 vaccines and treatments can prevent lasting symptoms

Instructing our cells to make specific proteins could control influenza, autoimmune diseases, even cancer

Different methods of drug delivery give us more tools to fight disease

Solutions to age-related vision problems now come in a bottle. How well do they work?

Hamsters eating Cocoa Krispies reveal inflammation pathways from the olfactory system to the brain

Endless boosting might not be a practical or sustainable strategy, scientists say

The huge jump in cases means more hospitalizations. And children’s small airways can be more easily blocked by infections

But shortages mean that new antivirals and other drugs may be hard to come by
Impaired blood flow leads to loss of limbs

Hopes are high for a class of drug that could treat neurodegenerative conditions—but a recent clinical trial has brought the field up short
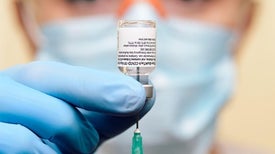
mRNA vaccines are now in the limelight as a key tool for tackling COVID-19, but the technology was originally developed for other diseases, such as cancer, that researchers are now hoping to treat...

Many do not require FDA approval, and those that do often do not undergo clinical trials

Heart disease risk increases as women get older, but explanations that center on changes after menopause don’t tell the full story

Researchers are debating how to convince the heart to heal itself instead of laying down scar tissue after a heart attack

Coronavirus infections might cause lasting harm to the heart even in those who have never had symptoms
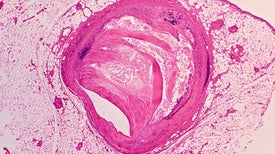
A high-fat diet is thought to increase the risk of a heart attack. But some say that the long-held dogma of “bad” cholesterol might be flawed

A type of immune-cell priming called trained immunity is helping researchers to understand the disease mechanisms behind the buildup of fatty deposits in arteries
Anti-inflammatory therapies for cardiovascular disease are nearing the clinic. But whether scientists understand how inflammation contributes to fatty-deposit buildup well enough to target it effectively is open to debate...
Lifestyle is a major contributor to heart disease in adults, but risk factors such as genetics and parental lifestyle can also have an effect
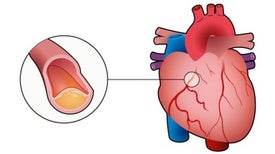
Globally, nine million people die each year from ischemic heart disease. Despite falling rates of heart disease, tackling it is still a stubborn challenge
Support science journalism.

Thanks for reading Scientific American. Knowledge awaits.
Already a subscriber? Sign in.
Thanks for reading Scientific American. Create your free account or Sign in to continue.
Create Account